Many people who hear the word ‘ultrasound’ will probably associate them with pregnancy scans, but this particular type of test can be used for much more than that.
At Echelon Health, we use ultrasounds to detect a range of different health issues. But just what can an ultrasound detect?
If you’re thinking about getting an ultrasound as a part of a preventative healthcare screening or as part of one of our health assessment packages, you may want some more information on how they work and why they are important.
What is an ultrasound and how does it work?
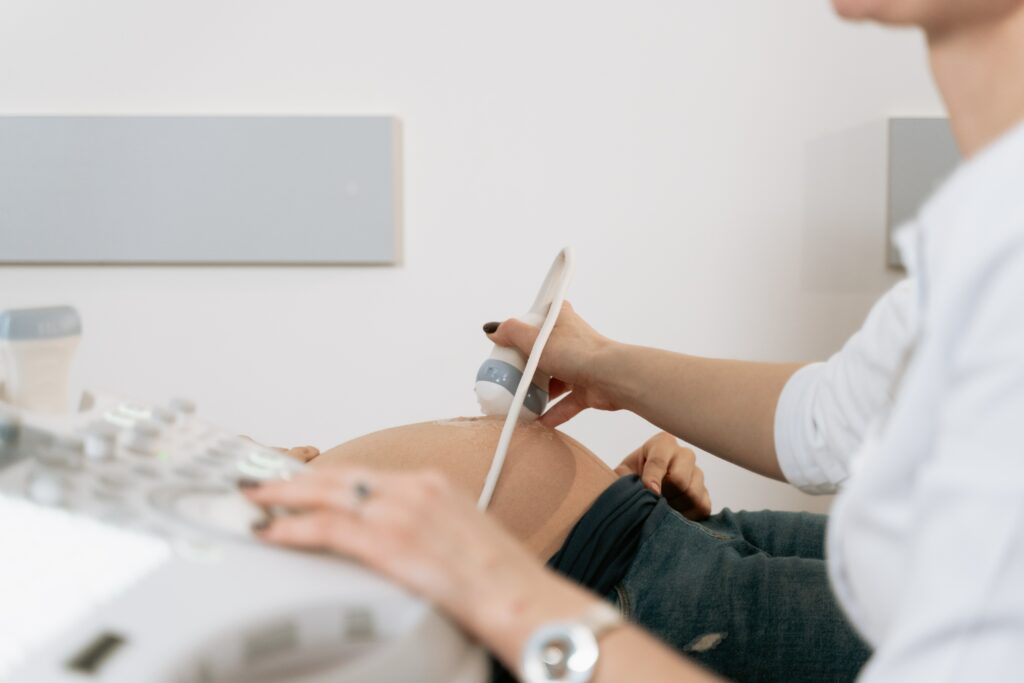
An ultrasound scan — also known as a sonogram — is a medical test that uses sound waves to create a live image of part of the inside of the body.
Ultrasound scans use a small device called an ultrasound probe to give off high-frequency sound waves. You can’t hear these sound waves because they are too high-pitched, but when they bounce off different parts of the body they create an ‘echo’; in the same way bats and dolphins use echolocation to hunt and move in pitch darkness.
These echoes are then picked back up by the probe and used to form a picture on a monitor. It’s a similar technology to that used by sonar and radar, which we use to detect objects like planes in the sky or ships out to sea.
Usually, a specially trained ultrasound technician (called a sonographer) will carry out your scan, but the image and results will be interpreted by your doctor or a radiologist
Unlike other imaging techniques such as X-rays or CT scans, ultrasounds don’t use any radiation and are very low-risk. This is why we use this type of scan to monitor an unborn baby during pregnancy.
What does an ultrasound show?
The high-frequency sound waves that an ultrasound scan uses pass through fluids and soft tissues in the body and bounce back off denser tissues. This allows your doctor or a medical specialist to take a closer look at organs, tissues and body vessels to identify any conditions or abnormalities — all without needing to make an incision.
Ultrasounds are a multifunctional tool used to diagnose a number of conditions, spanning across a range of locations throughout the body. Here are some of the different locations and parts of the body that an ultrasound can be performed on:
- Heart
- Blood vessels
- Bladder
- Thyroid
- Liver
- Kidneys
- Gallbladder
- Spleen
- Pancreas
- Eyes
- Muscles, joints and tendons
- Ovaries
- Uterus
- Testicles
An ultrasound can pick up all of the above organs and body parts, and therefore be used to diagnose a wide variety of issues or conditions in these areas.
Ultrasounds don’t work on every part of the body; sound waves don’t transmit well through air or dense bone, so they aren’t effective at imaging body parts that hold gas (such as the bowel) or are hidden by bone (such as the head).
What can an ultrasound detect?
Ultrasounds can be used to detect and diagnose a range of different health conditions, such as:
- Cancer: ultrasounds can contribute to the detection of some types of cancer, such as liver cancer or testicular cancer. They can detect denser areas of tissue in certain body parts (such as the ones we’ve mentioned above), which may be tumours.
- Cysts: an ultrasound can also pick up cysts. They can determine the composition of a lump and help your doctor distinguish between a tumour and a cyst so that they can make a diagnosis.
- Cardiovascular issues: ultrasounds can detect a variety of cardiovascular problems, such as narrowed blood vessels, blockages, heart defects and heart disease.
- Uterine fibroids: if you are suffering from pelvic pain or abnormal periods, an ultrasound can be used to find the source of the problem. Fibroids, cysts and other conditions associated with the female reproductive system can all be detected with an ultrasound.
- Thyroid conditions: ultrasound scans may be used to detect thyroid issues such as growths or abnormal activity. The test will also help them determine if a thyroid nodule needs a biopsy.
- Infections: Some types of ultrasound can contribute towards diagnosing infection.
- Liver problems: an ultrasound may be done to detect liver problems such as fatty liver disease, fibrosis or cirrhosis (scarring of the liver).
- Kidney problems: ultrasounds can also be used to detect kidney stones, cysts, tumours and infections in the kidneys.
- Gallstones: gallstones are usually confirmed using ultrasound.
This list isn’t definitive; ultrasound scans can be used to detect and diagnose a range of conditions related to your tissues or organs in the body.
Ultrasound accuracy
Ultrasounds can help doctors and specialists to detect conditions and problems that might not necessarily show up on X-rays or other types of scans. They can also help to pinpoint the location of the issue — such as where a tumour or cyst is — and guide instruments during biopsies (which is when a small amount of tissue or fluid is removed from the body to be studied).
On the whole, ultrasound accuracy is high — especially when used in conjunction with other imaging technology.
At Echelon Health, we recognise that there isn’t just one type of scan that can be used to detect all health conditions or diseases, which is why we use multiple imaging technologies, which includes Ultrasound, CT, MRI and a comprehensive set of blood tests to carry out our health assessments and ensure our clients are receiving the gold standard when it comes to assessing organs of the bod and detecting diseases at their earliest stage.
These high-quality images and results are then analysed by our select team of internationally renowned specialists, who will then provide an in-depth health report and advise on the results and treatment that may be needed.
Ultrasound vs CT scan: what’s the difference?
There are a few differences between ultrasound and CT scans (computerised tomography scans).
Ultrasounds are very low risk because they don’t involve exposure to radiation. There are no known risks from the high-frequency sound waves used in an ultrasound.
Ultrasounds are generally painless and don’t cause side effects. They are typically slightly longer than CT scans — a routine ultrasound can last any time from 15 minutes to one hour.
On the other hand, CT scans use X-rays to create a detailed image of the inside of the body. There is a very small risk associated with the X-ray radiation that you are exposed to in a CT scan. However, CT scanners are specially designed to ensure that you’re not exposed to unnecessarily high levels of radiation, and they are generally very safe.
CT scans are quick, lasting for around 10 to 20 minutes.
Advantages of an ultrasound
Ultrasound scans offer many advantages and can be extremely beneficial to the patient.
Here are some of the advantages of an ultrasound:
- Ultrasounds are extremely safe as patients are not exposed to radiation (as they are in X-rays and CT scans)
- There are typically no side effects from ultrasounds
- Ultrasounds are usually painless and non-invasive (which means they don’t use needles, injections, or create incisions)
- Ultrasound scans capture live images of soft tissues that don’t show up on other types of imaging tests like X-rays
- Ultrasounds can be used to diagnose many different types of health conditions or possible issues before they become too high a risk
Health assessments at Echelon Health
As the world’s leading health assessment provider Echelon Health believes that there is no ‘one size fits all’ approach when it comes to health. We do our best to equip you with the best understanding of your health. We have several different packages that would provide information about your area of concern.
Our Core Cancer package aims to detect cancers at their earliest possible stages. It detects several cancers including leukaemia, breast, prostate, colon, liver cancer and more. Here is what is included in our Core Cancer assessment:
- Blood tests
- CT abdomen
- CT pelvis
- CT virtual colonoscopy
- MRI prostate
- Ultrasound thyroid
- Ultrasound testes/ovaries
- Digital mammogram
If it is complete peace of mind that you are after, our Platinum Assessment is one of the most comprehensive in the world and looks at your body head-to-toe. Using fully comprehensive blood tests in combination with the most advanced imaging technology through CT, MRI and ultrasound scans, we are able to detect up to 92% and 95% of the causes of premature death among men and women respectively. The following scans are part of the Platinum Assessment:
- Blood Tests
- ECG
- CT Aorta
- CT Heart
- CT Coronary Angiogram
- CT Chest
- CT Pelvis
- CT Virtual Colonoscopy
- CT Bone Density
- EOS
- CT Upright Skeleton
- MRI Brain
- MRI Cerebral Artery Angiogram
- MRI Carotid Artery Angiogram
- MRI Prostate
- Ultrasound Thyroid
- Ultrasound Testes/ Ovaries
- Digital Mammogram
- Full Body Mole Screen
If you are curious to find out more, do not hesitate to contact us any time and we will be happy to help you.
Sources: