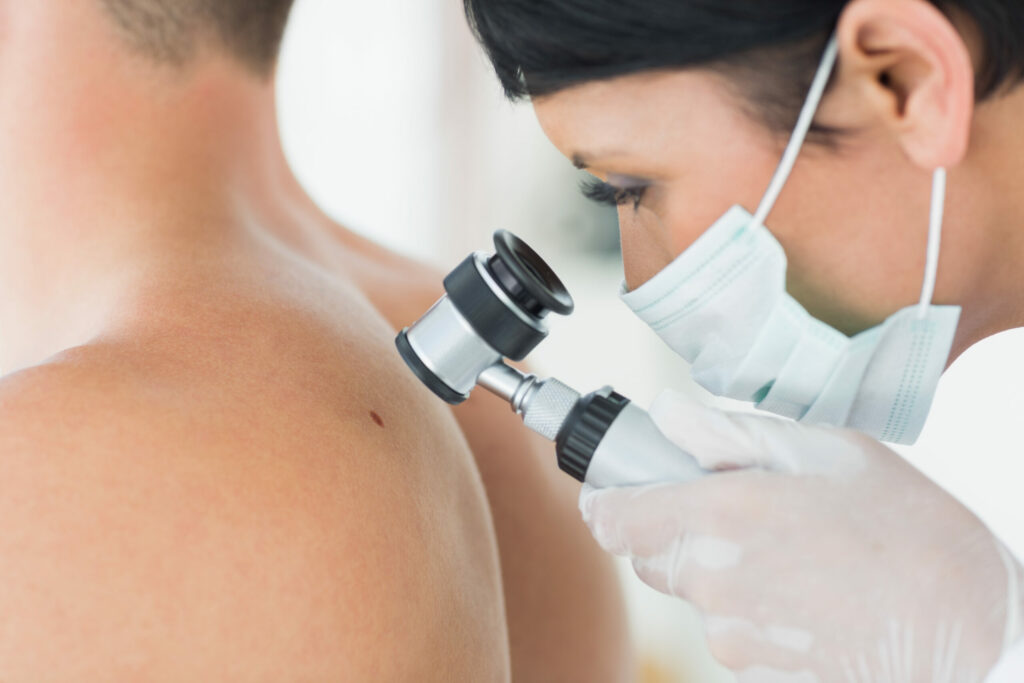
Skin cancer impacts over 100,000 people every year in the UK and, although it’s one of the most common types of cancer, it’s also one of the most preventable.
Often associated with the sun, skin cancer is caused by overexposure to the sun’s ultraviolet (UV) rays, resulting in damage to the DNA in skin cells.
But that doesn’t mean you should avoid setting foot outside.
Read on to discover more about the link between sun exposure and skin cancer with Echelon Health, and learn how to make the safest choices for your skin’s health.
What is sunburn?
Sunburn is a skin condition caused by overexposure to UV radiation from the sun or other sources, such as tanning lamps. It’s characterised by red, painful, and sometimes blistered skin, which may feel hot to the touch.
When skin is exposed to UV radiation, it triggers the production of melanin. This is a pigment that gives skin its colour and protects it from further damage.
However, if the exposure is too intense or prolonged, the skin may not be able to produce enough melanin to prevent damage, resulting in a sunburn.
The severity of sunburn can depend on factors such as:
- Skin type — people with lighter skin are more susceptible to sunburn
- The intensity of UV radiation
- Duration of UV exposure — sunburn can occur in as little as 15 minutes of exposure to UV radiation
As well as the immediate pain and discomfort that sunburn can cause, it can also have long-term effects on the skin.
What is UV?
UV radiation is a type of electromagnetic radiation emitted by the sun and man-made sources like UV bulbs. It is invisible to the human eye.
UV is classified into three types — UVA, UVB and UVC.
- UVC is largely absorbed by the Earth’s atmosphere and does not reach its surface
- UVA and UVB can penetrate the atmosphere and reach the Earth’s surface
UVB causes most sunburns, whereas UVA ages the skin.
The intensity of UV radiation varies depending on factors such as the time of day, the season and the location. UV radiation is strongest during the middle of the day (between 10 am and 4 pm) and is more intense at higher altitudes and closer to the equator.
Can UV cause skin cancer?
Yes, UV radiation can cause skin cancer. When your skin is exposed to UV radiation, it damages the DNA in the cells. This can then lead to mutations and the development of cancerous cells.
The risk of developing skin cancer depends on factors such as:
- Skin type — people with lighter skin and light-coloured eyes are more susceptible to skin cancer
- Repeated sunburns
- History of tanning bed use
- Family history
- Amount of UV exposure
Types of skin cancer
There are three main types of skin cancer — basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma and melanoma.
Basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma are the most common and usually develop on areas of the skin frequently exposed to the sun, such as the face, neck and hands.
Melanoma is less common but more dangerous, as it can spread to other parts of the body. It can occur anywhere on the body, even in areas that aren’t exposed to the sun.
Can you get skin cancer from sunburn?
Sunburn is a clear sign that the skin has been damaged by UV radiation, which increases your risk of developing skin cancer.
Repeated sunburns over time can also increase skin cancer risk, so it’s important to protect your skin and regularly check it for any changes or abnormalities.
Consult a doctor if you notice any changes, no matter how small they may be. Early detection is key to successfully treating skin cancer.
Who is at risk of getting sunburn?
Anyone exposed to the sun can get a sunburn, but certain factors increase the risk. Those most susceptible include:
- People with lighter skin and eyes
- People with thinner and more delicate skin, such as children or elderly people
- People who work or spend a lot of time doing outdoor activities
- People who live in areas with a high UV index, such as near the equator or at higher altitudes
- People who take medications that make the skin more sensitive to UV radiation
- People with skin-related medical conditions, like rosacea
How to treat sunburn
If you do get sunburnt, there are several ways to treat the symptoms and help your skin heal.
- Find shade — get out of the sun and into a cool, shaded area to prevent further damage to the skin.
- Drink water — drink plenty of water to prevent dehydration as this can make sunburn symptoms worse.
- Take pain relief — medications like paracetamol and ibuprofen can help alleviate pain and reduce inflammation.
- Use a cold compress or aloe vera — applying a cool, damp compress, or an aloe vera gel or cream, to the affected area can soothe the skin and reduce discomfort.
- Avoid further sun exposure — stay out of the sun until the skin has fully healed, as continued UV exposure could increase your skin cancer risk.
If your sunburn is severe and blistering, or if you experience a fever or vomiting, seek medical advice as soon as possible — this could be heat stroke.
Mole screening and skin cancer prevention
Moles are more than just little marks on your skin — they can be useful indicators when monitoring your skin’s health.
Changes in your moles can be a precursor to skin cancer, so you must keep an eye on them.
At Echelon Health, we offer full-body mole screening in our platinum package at our state-of-the-art Mole Clinic.
As leading skin cancer screening and mole removal specialists in the UK, our expert team deliver top-quality clinical care and skin cancer screening to over 40,000 patients every year.
By having your moles regularly checked by a medical professional, you could reduce your chance of skin cancer and even prevent it.
Changes in your moles you need to look out for include:
- Irregular shapes or being different on each side
- A notched or jagged border
- Colour — this can be a change in total colour or the mole is a mix of two or more colours
- Size — changes in size, such as growing larger
If you notice any changes to any of your moles, book a mole screening appointment as soon as possible.
How to reduce the risk of getting skin cancer
There are several ways to reduce the risk of getting skin cancer:
- Limit sun exposure — avoid prolonged exposure to the sun during peak hours and seek shade whenever possible.
- Wear protective clothing — long-sleeved shirts, trousers, sunglasses, swimwear and wide-brimmed hats can protect against UV radiation.
- Use sunscreen — using a high SPF (30 or higher) can help to protect the skin from UV radiation. Apply sunscreen at least 20 minutes before going outside and reapply every two hours or more frequently if swimming or sweating.
- Avoid tanning beds — tanning beds emit UV radiation that can increase the risk of skin cancer so should be avoided.
- Perform regular skin checks — regularly checking your skin for any unusual moles or changes in existing moles can help detect skin cancer early. You should ideally perform a self-exam every month and see a medical consultant annually for a full skin exam.
Get in touch with Echelon Health
If detected early, skin cancer is very curable. In many cases, biopsies can not only successfully diagnose skin cancer but also successfully treat it. It is imperative that you consult a medical expert if you observe any changes in your skin, painful or not.
Here at Echelon Health, we offer a comprehensive service screening the entire body for possible skin cancer. As part of our Platinum Assessment package, we work together with The Mole Clinic, an award-winning, dermatologist-led skin lesion clinic. Their specialist nurses, consultant dermatologists and plastic surgeons deliver high-quality clinical care to 40,000 patients every year.
But skin cancer is just one of the cancers that our flagship Platinum Assessment package is able to detect. Using the best imaging technology available, our MRI, CT, and ultrasound scanners we can detect liver, lung, breast, prostate cancer and more as well as other diseases such as coronary heart disease. In fact, we are able to detect up to 92% and 95% of preventable causes of death among men and women respectively. The following scans are available in the Platinum Assessment:
- Blood Tests
- ECG
- CT Aorta
- CT Heart
- CT Coronary Angiogram
- CT Chest
- CT Pelvis
- CT Virtual Colonoscopy
- CT Bone Density
- EOS
- CT Upright Skeleton
- MRI Brain
- MRI Cerebral Artery Angiogram
- MRI Carotid Artery Angiogram
- MRI Prostate
- Ultrasound Thyroid
- Ultrasound Testes/Ovaries
- Digital Mammogram
- Full Body Mole Screen
If you want full peace of mind and to ensure your health is optimal from head-to-toe, please get in touch with our team to learn about other packages or book yourself in for a full body MOT today.
Sources:
- https://www.skincancer.org/risk-factors/sunburn/
- https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/sunburn/
- https://www.webmd.com/beauty/sun-exposure-skin-cancer
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/10985-ultraviolet-radiation
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC113773/
- https://www.cancerresearchuk.org/about-cancer/causes-of-cancer/sun-uv-and-cancer/